the principle of cross-rate in the foreign exchange market
By The Forex Review - 17 / May / 22 590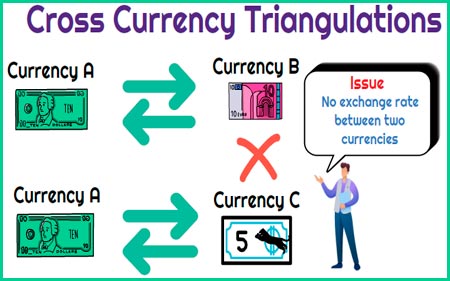 Dominick Bell
Dominick Bell
A cross rate is the rate of one currency against another, calculated from the rate of these two currencies against the common currency. This is called the cross price method or indirect quotation.
Most of the currencies of indirect quotes are made through the dollar, which is the "base" currency of the international monetary system.
There are also direct quotes between some of the major currency pairs such as EUR/USD, EUR/CHF, USD/JPY, etc.
Foreign exchange market: cross rate principle
In the forex market, the most traded currencies are called "major currencies".
Good to know: In addition to the US dollar, the most traded currencies are the Euro (EUR), Japanese Yen (JPY), Pound Sterling (GBP), Swiss Franc (CHF) and Australian Dollar (AUD). Including US dollars, these six currencies have monopolized almost 90% of trade.
Given the dominance of the US dollar, the cross rate (the exchange rate of one currency against another) is calculated based on the exchange rate of these two currencies against a common currency, often the US dollar.
The advantage of this cross rate ("cross rate") is that it allows you to price all currencies, even if they are not directly quoted to each other when the market changes.
Example: I'm asking a forex trader to provide spot quotes for currencies A and B because that quote doesn't exist directly.
Good to know: A forex trader is an operator whose function is to permanently fix the exchange rate of one or more convertible currencies.
To do this, the forex trader will use the quote currency common to A and B: this currency C will usually be the dollar.
In specific terms (a simple cross rate), a forex trader would apply the following formula:
Currency A Currency A Currency C
Currency B Currency C Currency B
Good to know: Many online calculators allow you to calculate cross rates. The date of the exchange rates used should be reviewed.
Cross quotes: from indirect quoting to direct quoting
In the forex market, some currencies are constantly quoted against each other. These are the "major" currencies. In these pairs, the base currency is called the "base". In most cases, this is the US dollar. For its part, the currency that is quoted against the base currency is called the "counterparty". The price of these pairs results in a quote.
Good to know: There are 18 major currency pairs in Forex.
Note. Forex (for Foreign Exchange) is an over-the-counter market where most of the world's currencies are traded at constantly changing rates.
When buying or selling a currency pair, each has a buy and sell rate. The difference between the buy price and the sell price is called the spread.
The price of a currency pair is unstable and constantly changing. Forex traders make money through various strategies such as buying a pair and then selling it at a higher rate, or selling a pair before buying at a lower rate.
For your safety, we have compiled a blacklist of brokers.







